Payment gateways are like old post offices. They’re still functional. Not only that, but they are filled with letters, parcels, and busy workers. They sort packages, group items, and hand them out for delivery—by cars, trains, airplanes, and sometimes even dogsleds, but only if you’re at the Pole.
Payment gateways work the same way. They gather transaction data, sort it out, and send it to the recipient’s bank account, keeping everyone in the loop along the way.
A payment gateway is some kind of instrument or gear, if you wish. It transfers data on transactions between banks, customers, buyers, and sellers. In essence, it is an intermediary that stands between the buyer and the seller.
Just imagine, specialists estimate the volume of electronic payments $2.17 trillion. A huge amount considering that PayTech accounts for only 25% of all transactions.
In this article will explore the main things of payment gate integration and its benefits to business with right implementation.
Everynone now has experienced such payments, in online stores, paying for services, using a bank card or e-wallet.
Integration includes gateway selection, interface customization, security. The last stage involves testing and launching.
In essence, payment gateways are the core element of PayTech (Payment Technology) infrastructure, and serve for accepting and processing wire transfers. Let’s take a closer look at what functions payment gateways perform in online transactions:
- Data encryption.
- Routing.
- Authorization.
- Feedback.
Why do you need online payment gateway integration?
It stands to reason that in e-commerce, payment gateway integration is a must-have. A properly integrated payment system means reliability, security and customer trust. In today’s world, you can’t imagine bank or e-commerce without payment gateways.
Main advantages
The main benefit of payment gateway integration is the customer experience. Users can easily pay for purchases in online stores, quickly transfer money to each other, pay for utilities, and so on. All of this would not be possible without payment gateways.
High speed payments. Forget about slow bank transfers that take 3-5 business days. Today, money can be transferred instantly thanks to p2p payments, by phone number or email. Thanks to payment gateways!
Multicurrency. For example, PayPal supports 25 currencies, among them USD, EUR, GBP, CAD, AUD, JPY. Through Stripe you can transfer money in 135 currencies. Supporting multiple currencies opens up unlimited opportunities to capture foreign markets.
Impact of payment gateway integration on business profitabilityAmazon created and implemented its own payment gateway, Amazon Payments. A verified Amazon account is enough to use the payment process. Integrating the gateway on third-party sites boosts transactions and profits.
Airbnb once faced the problem of international payments. The integration of Stripe‘s payment gateway solved this problem. It allowed to accept local currencies and processed payments quickly. As a result, Airbnb could launch into new markets.
These examples show that modern business requires payment gateways. Especially when it comes to international transfers.
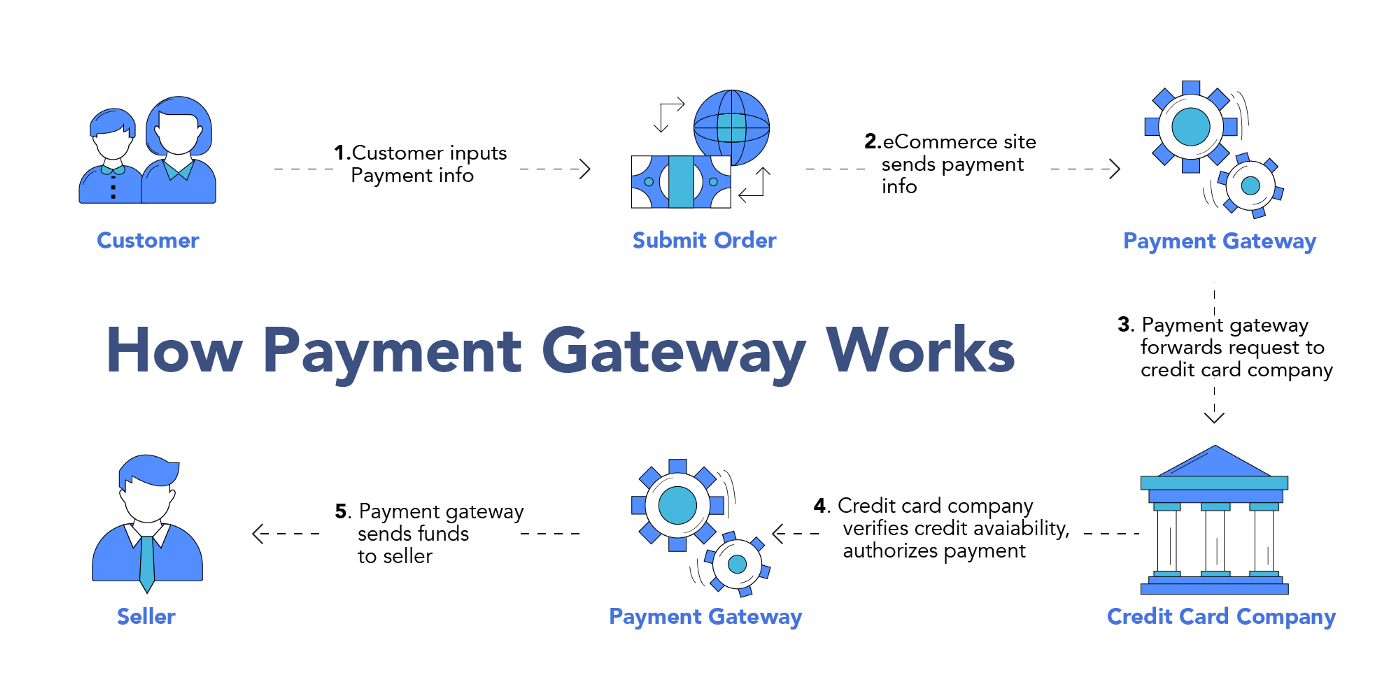
How do payment gateways work?
From the client’s side everything looks quite simple! He opens an window, in which you are offered to choose a payment method and fill in a form, for example, bank card details. Card number, owner’s name, expiration date, CVV code.

An example of a Visa card with data to process a transaction
However, all the magic is hidden from the eyes of the average user. Nuances are essential, and many things happen unnoticed. Allow me outline what happens after a client enters their card information and starts a payment.
- Encryption of payment data. SSL/TLS encryption is used for secure transmission of information over the Internet.
- Transmission of data to the bank. Encrypted data is transmitted from the payment gateway to the merchant’s bank, which is responsible for processing the transaction.
- Data validation and routing. At this stage, the merchant’s bank sends the data to the correct payment system, such as Visa or Mastercard. After that, the payment system redirects the data again, but already to the bank that issued the card.
- Notification. If the transaction is processed successfully and no errors, the payment gateway receives a notification. If errors were detected during data processing, a notification from the payment gateway appears on the screen.
- Transaction completion. If the transfer is successful, the funds on the client’s account are frozen and sent to the merchant’s account.
As a rule, it takes a few seconds to complete transactions.
Varieties of payment gateways
Payment gateways come in several types. Let’s analyze in detail the most popular of them. Let’s determine the advantages and disadvantages.
Hosted Payment Gateways (Hosted Payment Gateways)
The peculiarity of this type of system is that the form or page of the gateway is located on the server of the provider (bank). But the merchant can integrate it into his site using an iframe or redirect. Examples of such payment gateways are Worldpay, 2Checkout.
Worldpay payment gateway
Advantages. Simple integration. High security (data does not pass through the merchant’s server). Multicurrency, many payment methods.Disadvantages. Lack of possibility to customize the interface on the seller’s side. Minimal control over transactions.
Advantages. Simple integration. High security (data does not pass through the merchant’s server). Multicurrency, many payment methods.
Disadvantages. Lack of possibility to customize the interface on the seller’s side. Minimal control over transactions.
Local bank integration
Such payment gateways can provide access to local banks and payment methods that are popular in a particular region. Examples of such payment gateways: Cielo (Brazil).
Advantages. Support of national currencies, payment methods popular in the region, banks. Optimized solutions for comfortable work in a given region.
Disadvantages. Limited support for international payments. Difficulties of integration with global platforms.
Direct Post Method
This method of integration provides transfer of payment information directly from the merchant’s server to the payment gateway server. Examples of payment gateways supporting the direct post method are Authorize.Net, Stripe, PayPal.
Advantages. Simple integration. Full control over the interface, it can be changed at will. Control over transactions. High speed of payment processing.
Disadvantages. Increased security requirements. Vulnerability to attacks. Lack of protection from the payment gateway. In case of failure, the entire payment processing system will be unavailable.
API Integration (Direct/Post API Integration)
This method works as follows. Payment information is transmitted to the merchant’s server, then sent to the bank’s processing center through the payment gateway API. Examples of payment gateways that support API integration include Stripe and Braintree.
Advantages. The merchant gets full control over the interface. You can add additional modules, change the appearance. Control over transactions. Adding additional features.
Disadvantages. Integration requires specialists who understand the API and can maintain and modify the payment gateway. Higher security requirements, in particular PCI DSS.
Integration with a mobile payment gateway
This method allows you to conduct transactions through your cell phone, connecting to systems such as Apple Pay, Google Pay and the like. Mobile versions of the website and apps for iOS and Android are supported. Payment gateways that support integration are Square, Paytm.
Advantages. Support for advanced technologies, in particular mobile payments. Convenience for customers using cell phones for purchases and transfers.
Disadvantages. May have difficulties with traditional payment methods. Low support for desktop versions of websites, payment gateways. Users need to have a cell phone with them at all times.
Essential attributes of payment gateways
Here we come to the critical attributes of payment gateways. A modern payment gateway is not a mere conduit for transactions. It must meet a number of strict requirements. First and foremost, it must be secure. It also needs to be user-friendly, reliable and easily adaptable. These basic requirements should guide the selection of a gateway, namely:
Security and froud prevention. Payment gateways should have fraud detection mechanisms. Address verification system (AVS), and card authentication (CVV) and tokenization is a must. And all of this is also supported through the use of SSL encryption.
Easy integration and payment flexibility. For payment gateways that use APIs to connect to e-commerce platforms and shopping carts, this aspect is also extremely important. It is hard to overemphasize the importance for customers to be able to pay using both traditional credit, debit cards and bank transfers as well as cryptocurrency via e-wallets. In addition, the provision of the SDK allows developers to customize the integration, providing a user-friendly process that increases conversion rates.
User-centered interface. Latex gateway interfaces design should provide intuitive navigation and be so optimized to provide a fast checkout experience.
Always-On Customer Support. Reliable 24/7 customer support via phone, chat and email is essential and builds trust and confidence, encouraging customers to complete transactions knowing that help is always at hand.
Advanced reporting and billing features. Providing analytics and reporting gives you valuable information to make the right decisions. In addition, automatic recurring billing simplifies the payment process. This, of course, increases efficiency and customer satisfaction. This combination ensures timely payments.
System reliability and performance. These qualities are designed to reduce transaction processing delays. Payment gateways must be able to handle peak loads. And payment gateways should have backup systems to overcome emergencies.
All of the above measures can ensure customer satisfaction, which certainly affects their trust and leads to increased sales.
Considerations Before Choosing a Payment Gateway Provider
Now that you’re familiar with the attributes of payment gateways, it’s time to look at choosing a provider. Here are some of the most important factors to consider.
1. Study the Pricing
Payment processing involves several financial institutions, each charging fees for their
services. Common fees include setup and monthly gateway charges, merchant account
setup, and transaction fees. Be sure to read all pricing documentation to avoid hidden
costs.
2. Examine Merchant Account Options
You can obtain one through banks or providers that include it as part of their service. If you don’t have an account, consider choosing a provider that offers one.
3. Check Transaction Limits
Gateway providers set minimum and maximum transaction limits that can affect your
choice. For example, Stripe has a minimum of $0.50 and a maximum of $999,999.99.
Ensure the limits align with your business needs, especially if you sell low-cost items or
have daily/monthly limits.
4. Payment method support
Make sure the payment gateway supports the main methods: credit cards, which remain the most popular payment method and electronic payment methods such as PayPal. Also, make sure the gateway offers multi-currency support for international sales, as many vendors do.
5. Mobile payment options
Mobile payments such as Apple Pay and Google Pay have their own tokenization processes and require special support. Check to see if the vendor supports these wallets and associated transaction limits, as these can vary from service to service.
How to choose the right payment gateway for integration
Selecting and integrating a payment gateway is a very important step for a business. First of all, it is necessary to understand what is required from the payment gateway. For example, if you plan to enter new markets, you need to assess the system’s ability to support regional payment methods and national currencies. It is not superfluous to study the tariff schedule, which may include commissions for money transfer and currency conversion, refunds.
It is important that the payment gateway complies with PCI DSS security standards. Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard is designed specifically to protect payment card information (Visa, MasterCard, American Express, Discover and JCB). CVV-CVC codes are not stored on the site. Many regulators require compliance with such standards and it is mandatory in almost all countries.
Here are examples of a few popular payment gateways.
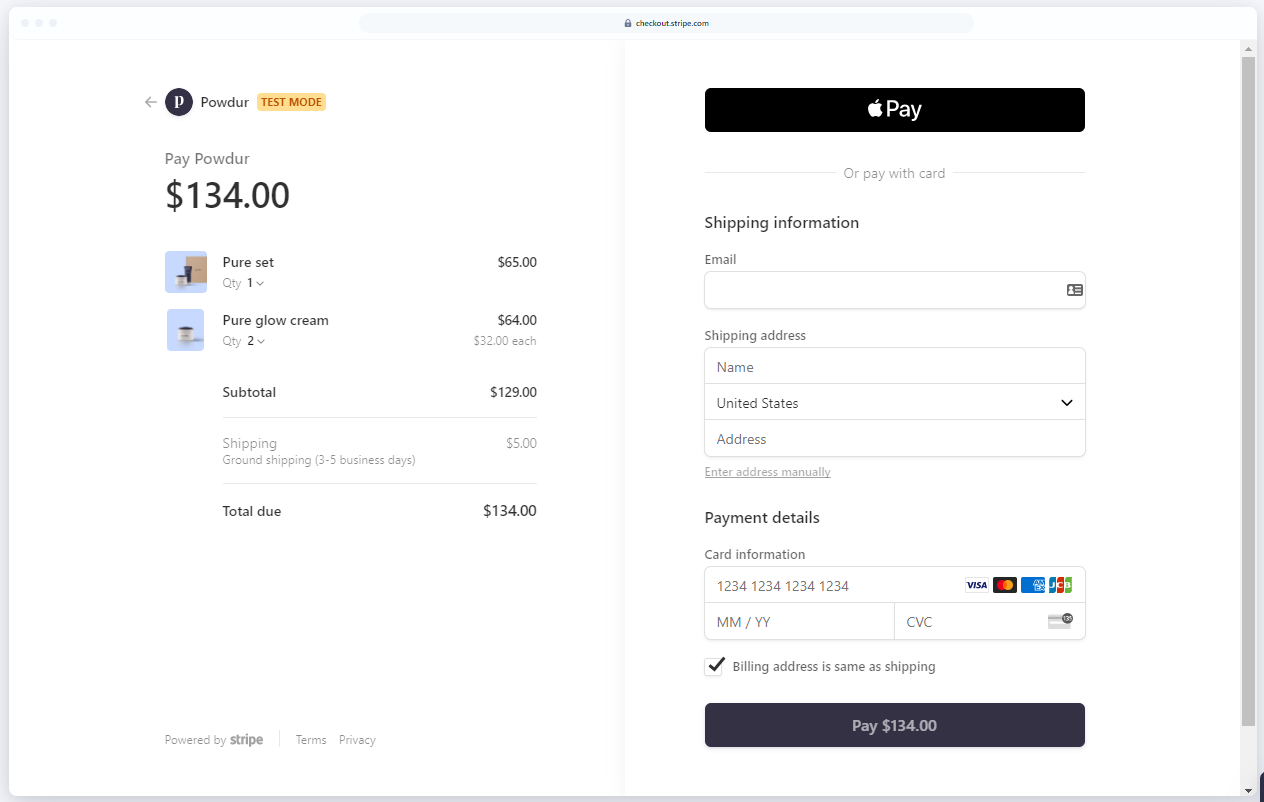
Stripe payment gateway screen
Stripe does not charge a subscription fee for using its gateway, however, it does charge transaction fees: In the U.S., the fee is 2.9% of the transaction amount + $0.30 per successful payment. In Europe and other countries that support the Euro, the fee is 1.4% of the transaction amount + €0.25 per successful payment if the card is issued in Europe. If the card is issued outside Europe, the fee will be 2.9% + €0.25. In other countries, the fee may vary, but is usually around 2.9% + a flat transaction fee (e.g. $0.30 or local currency equivalent). The system supports 30 languages and 135 currencies.
Paypal. One of the largest payment systems in the world. Allows you to install an integrated payment gateway on your site.
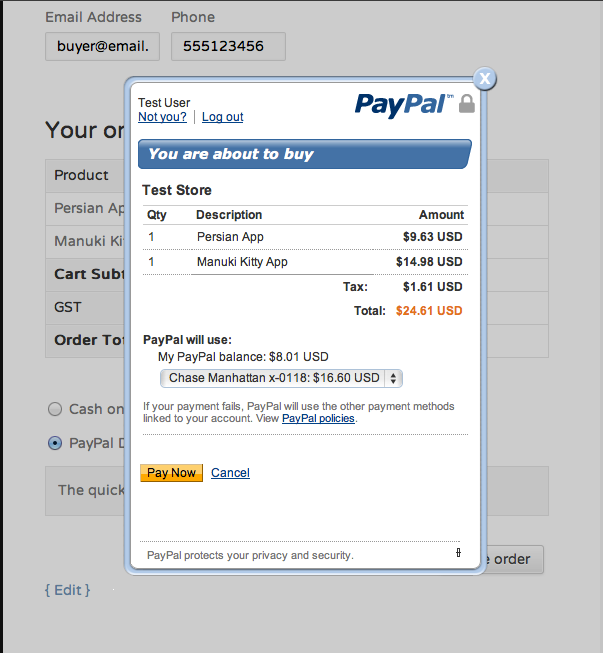
Example of payment via Paypal payment gateway
There are two plans for sellers. Basic, which is free, and PayPal Payments Pro with additional functionality for which you have to pay $30 per month. Paypal has no setup and maintenance fees, however, the system may charge fees for successful transactions and currency conversions.
Paypal supports more than 20 currencies and over 25 languages. Users are offered various payment methods: bank cards, transfers. It is possible to integrate local payment systems. Google Pay and Apple Pay e-wallets are supported.
Popular Payment Gateway Providers
There are tons of gateway providers and to color up the idea of their work please find most representative ones.
| Features | PaymentMethods | Gateway Features | Fee per Transaction |
| Stripe | AliPayAndroid PayApple PayBitcoin, ACH,WeChat, EPS | PCI DSS compliance,AVS, SSL, CCV,Virtual Terminal | 2.9% + $0.30 |
| PayPal | Android PayApple PayBitcoin, PayPalVenmo | PCI DSS compliance,AVS, SSL, CCV,Virtual Terminal | 2.9% + $0.31 |
| AmazonPay | AmazonPay | PCI DSS compliance,AVS, SSL, CCV | 2.9% + $0.32 |
| Authorize Net | Apple PayPayPal, E-Check,Visa Checkout | PCI DSS compliance,AVS, SSL, CCV,Virtual Terminal | 2.9% + $0.33 |
| 2Checkout | Wire, PayPal,WebMoney,Payoneer,WeChat | PCI DSS compliance,AVS, SSL, CCV | 3.5% + $0.35 |
Stripe is perhaps the best-known e-commerce solution with a easy-to-follow PCI compliance process. It accepts all major payment methods. Has mobile options as well as international support. It includes full documentation.
PayPal is one of the most widely accepted payment methods in the world and is suitable for businesses of all sizes.
Amazon Pay: originally developed for Amazon, is widely used for online stores. Integrates via API. More designed for mobile use.
Authorize.net is a good solution for small and medium-sized businesses, supporting basic payment methods, also having an Advanced Fraud Detection Suite feature
2Checkout is a great choice for businesses of all sizes. So it offers customizable packages that allows business handles their payment processing needs to meet changing circumstances. This means it helps you work more efficiently and makes it easier to expand into new markets or add new products.
Payment gateway integration process
Payment gateway integration consists of different aspects, including technical and legal. It all starts with designing the integration. The initial step is to study the requirements, analyze the goals and objectives, transaction types, and study the audience.
Implementation of the integration. At this stage, you need to register on the website of the selected payment gateway. After creating an account, you need to choose the type of integration and get API keys. In case of API integration, you need to customize the interface, payment form, connect modules, payment types.
Testing and deployment. This stage of integration includes the creation of test accounts. Verification of transaction processing without real payments. Refunds, cancelations, successful payment processing are checked. The error handler and analyzer are tested.
Routine maintenance and support. To keep the payment gateway functional, it must be properly maintained. Regularly create backups, install updates, analyze error reports (logs). This also includes regular auditing of PCI DSS requirements, CVV card codes should not be stored on the site. Regular security audits will increase customer confidence.
Documentation. Technical documentation includes architecture description, API. Data structure description, system requirements, upgrade instructions. Documentation for clients (users) should include detailed instructions on how to work with the payment gateway. How to fill out the form correctly, examples. FAQ so that the user can solve simple problems on his/her own without resorting to technical support.
Payment Gateway Integration Cost
The cost of creating and integrating a gateway depends on many factors. First of all, it depends on the features and complexity of the integration. It also depends on the provider. You can see how setup fee, monthly fee, transaction fee and other costs vary in the table above.
We can consider Development Costs. If we are talking about creating a custom payment gateway from scratch, the average MVP development cost will be from $150k to $200k, and the full solution will cost from $200k to $300k, as mentioned, depending on the complexity and functionality.
The integration itself will cost from $20,000 to $100,000, also depending on the complexity.
Final Words
In e-commerce and other businesses payment gateways is crucial point. Seamless payment gateway integration can significantly enhance customer experience that definitely lead increase sales.
With over 10 years of experience in software development, Itexus has gained deep expertise in all aspects of FinTech, including payment gateway solutions. When your business face a need in payment gateway integration, Itexus is here for your continence. And all you need is just reach out to us to get consultation from our top specialists. It helps you to prevent from mistakes whether it relates to off-the-shelt solutions or a custom-built system. Should you’re satisfied, we will be happy to be of service with any software development.
FAQ:
- How long does it typically take to integrate a payment gateway into an existing system?
Switching payment gateway providers can be complicated and may require significant effort, especially if the current integration is deeply embedded in the system. Businesses will need to re-evaluate their requirements, adapt the integration process for the new provider, and ensure that all existing customer data and transaction history are handled securely during the transition.
- What are some common challenges businesses face when integrating a payment gateway?
Some common challenges include compatibility issues with existing systems, ensuring compliance with security standards (like PCI DSS), and managing multiple payment methods and currencies. Additionally, businesses may face difficulties in customizing the user interface to maintain brand consistency or in testing the integration effectively without disrupting live transactions.
- Can a business switch payment gateway providers easily after integration?
Switching payment gateway providers can be complicated and may require significant effort, especially if the current integration is deeply embedded in the system. Businesses will need to re-evaluate their requirements, adapt the integration process for the new provider, and ensure that all existing customer data and transaction history are handled securely during the transition.
- Are there any specific industries that require specialized payment gateway solutions?
Yes, certain industries may need specialized payment gateway solutions due to regulatory requirements, payment types, or customer expectations. For example, industries like travel, gambling, and healthcare often face unique compliance issues and require gateways that can handle specific payment types (such as deposits or installment plans) or adhere to strict security standards.