As The Business Research Company states, by 2026, the digital banking market will hit $20 trillion—but here’s the kicker: 73% of SMEs already use it daily. Forget branch queues and paperwork—this is banking that operates at your speed.
In this article, we dissect:
- What a digital bank for business really is—and how its API-driven, cloud-powered engine outshines traditional banks.
- Why “digital” and “online” banking aren’t the same—and why it matters for your bottom line.
- What’s under the “Hood” of digital banking?
- What is on the user’s fingertips?
- Types of digital banks.
Ready to turn banking from a chore into your secret growth weapon? Let’s dive in.
What Is a Digital Bank for Business?
A digital bank for business operates online through apps and APIs, serving SMEs and startups. It replaces branches with instant account opening via AI-powered KYC checks. Without physical overhead, fees drop. Revolut Business automates multi-currency transactions; Mercury offers startup-friendly venture accounts.
Payments process faster using automation. Integrations with tools like QuickBooks sync data in real time. Support shifts to chatbots and in-app messaging. Traditional banks provide broader services (e.g., treasury management), but digital banks focus on core needs—checking, payments—while iterating rapidly. Built for speed, they scale with businesses, turning banking into a seamless, growth-focused tool.
What Are the Main Differences Between Digital Banking and Traditional Banking
Digital banking and traditional banking both serve financial needs but differ significantly in their approach. Below is a comparative summary:
| Feature | Digital Banking | Traditional Banking |
| Accessibility & Convenience | 24/7 access via mobile & web platforms; no need for branch visits. | Limited to branch hours; in-person visits often required. |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower operational costs due to no branches; lower fees and better interest rates. | Higher costs due to branch networks; fees for business accounts and transactions. |
| Customer Experience & Speed | Quick onboarding, instant transactions, AI-powered customer support. | Slower account opening, paper-based processes, in-person service. |
| Security & Trust | Advanced encryption, AI fraud monitoring, instant alerts; digital-only trust concerns. | Government deposit insurance, long-standing reputation, personal banking relationships. |
| Personalization & Services | AI-driven insights, automated financial tools, seamless fintech integrations. | Personalized in-person consultations, relationship-based banking. |
| Scalability & Innovation | Rapid adoption of emerging technologies (blockchain, AI, open banking). | Slower digital transformation due to legacy systems. |
In summary, digital banking offers greater convenience, often lower costs, and a tech-driven experience, whereas traditional banking offers physical presence and a legacy of trust. The trend is clearly toward digital – surveys show 61% of consumers are open to switching to a digital-only bank – but the best choice can depend on a business’s specific needs for service and features.
Digital Banking vs. Online Banking
While related, digital banking and online banking are not the same. The key differences lie in their scope and approach:
- Online Banking: Refers to accessing traditional banking services through the internet or mobile app, allowing customers to perform basic transactions like checking balances, transferring money, and paying bills. Online banking is an extension of traditional banking, offered by nearly every bank.
- Digital Banking: A broader concept that encompasses fully digital institutions and a complete suite of services enabled by technology. Digital banking provides advanced tools, such as AI-driven analytics, automated accounting integration, and personalized services, all through digital channels. It’s a digital-first approach that leverages open APIs, data analytics, and innovation to enhance the user experience.
For businesses, the distinction is crucial. Online banking might allow for routine tasks to be handled digitally, but digital banking offers a more integrated and innovative experience. Digital banking can provide features like real-time cash flow analytics, AI-generated financial health dashboards, and API integrations with accounting software, making it a more comprehensive and modern approach to banking.
In summary, online banking is a component of digital banking, providing access to traditional services through digital channels. Digital banking, on the other hand, reimagines the entire banking model to be digital-first, delivering greater value for tech-forward businesses.
The Benefits of Digital Banking for Businesses
Digital banking offers several advantages for companies.
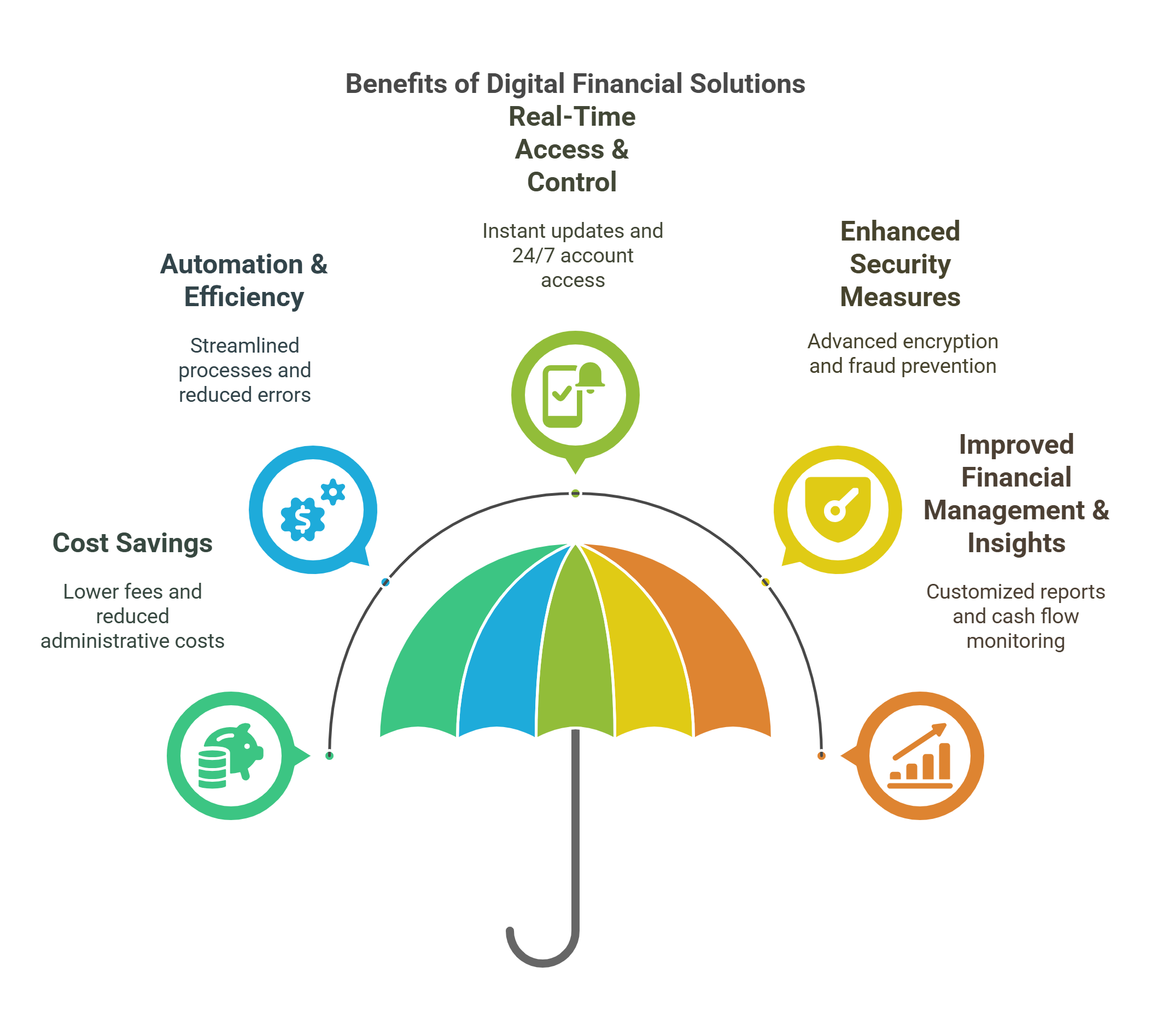
Cost Savings
Digital banking reduces costs through lower fees and competitive exchange rates. It also saves time by minimizing branch visits and paper check handling.
Automation & Efficiency
Digital banking automates financial tasks and integrates with accounting software. This minimizes errors and saves time through automated alerts and notifications.
Real-Time Access and Control
Digital banking provides real-time financial visibility and control. It enables instant fund transfers and online approvals.
Enhanced Security Measures
Digital banking uses advanced security measures to prevent fraud and breaches. It provides instant alerts and allows instant account lockdowns.
Improved Financial Management & Insights
Digital banking offers financial management tools with advanced analytics. It provides personalized insights to inform better business decisions.
Types of Digital Banks
Digital banks are not all the same. There are different models and players, each with unique characteristics.
Neobanks operate online without physical branches. They offer mobile apps or web platforms for customers to access banking services. Many neobanks focus on specific niches or underserved segments, such as retail consumers or freelancers. Neobanks often partner with licensed banks to handle regulated functions, which means customers’ funds are kept at the partner bank. They usually offer basic services like checking and savings accounts, payments, and cards. Examples of neobanks include Chime and Mercury in the US, and Revolut and N26 in Europe.
Challenger banks are fully licensed institutions that operate with a digital-first mindset. They offer a full suite of banking products entirely through digital channels. Challenger banks differentiate themselves by being user-centric, transparent, and technologically agile. They provide services like lending, international transfers, and multi-currency accounts with a better digital experience. Examples of challenger banks include Starling Bank and Monzo in the UK, and Varo Bank in the US.
Fintech companies offer banking-like services to businesses by partnering with banks. This is often called Banking-as-a-Service or embedded banking. Non-bank platforms provide financial accounts and payment services to users, with an actual bank powering those accounts behind the scenes. For example, Shopify offers business checking accounts and debit cards to its merchants through a partnership with a bank. Square and Brex also provide banking services to small businesses and startups through partner banks. These fintech-powered solutions blur the line of what is a bank, but deliver many of the same benefits of digital banking.
Traditional banks like JPMorgan Chase and HSBC are evolving into next-gen digital leaders by embracing advanced technologies while maintaining their legacy of security and reliability. They blend physical branches with seamless mobile/online platforms, offering trusted brand reputation alongside modern convenience. This hybrid approach positions established institutions as competitive players in the tech-driven banking era.
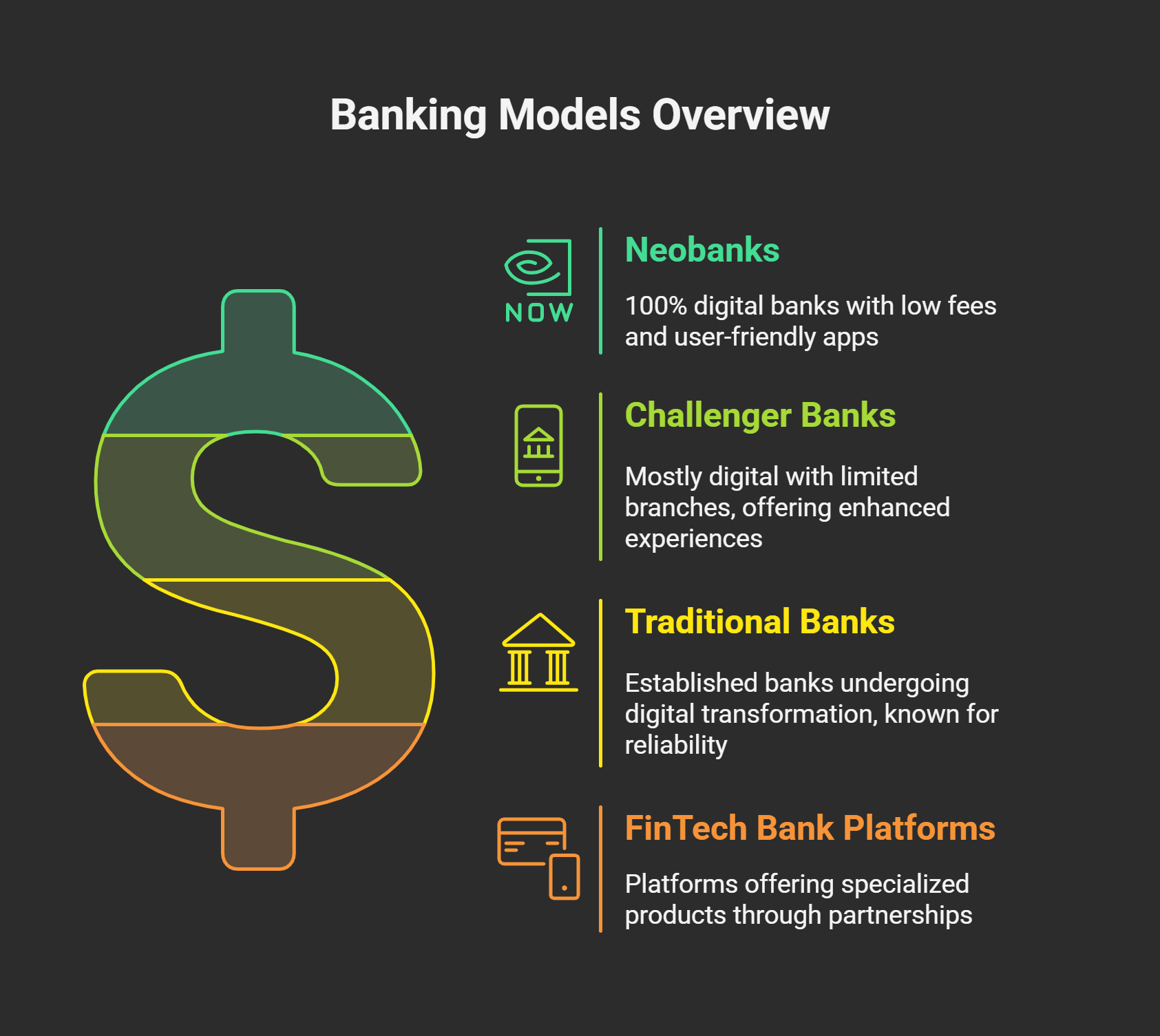
Businesses have multiple options for digital banking. They can choose a neobank for basic services with simple access. Challenger banks offer full-service banking with a modern twist. Fintech platforms incorporate banking into other business tools. All these reflect the broader shift in banking — away from traditional branch networks toward flexible, technology-driven solutions. As of 2023, there were over 230 licensed digital-only banks globally, and hundreds more fintechs offering bank-like services, underscoring that this is not a niche trend but a mainstream movement in finance.
What’s Under the Hood? Essential Features of Digital Banks
To provide digital banks with robust technical features, developers equip them with a range of essential functionalities that simplify financial management and empower businesses to operate efficiently. Below, we clearly outline the core digital banking functionalities that we often utilize and how they translate into practical benefits.
Digital Account Management
To streamline account management, digital banks must be able to handle banking entirely online:
- Easy online onboarding processes, allowing account opening within minutes.
- Digital Know Your Customer (KYC) using GBG for identity verification and IDology.com for Social Security Number (SSN) verification.
- Secure authentication frameworks, including OAuth2.0 supported by ForgeRock, ensuring data protection.
These features and instruments help businesses achieve quicker setups, reduce paperwork, and facilitate seamless, secure onboarding.
Fast Payments & Transactions
Digital banks provide fast and efficient payment processing through the following features:
- Near-instantaneous transaction capabilities for domestic and international payments through Real-Time Payments (RTP) networks and Automated Clearing House (ACH) APIs.
- Integration with modern payment gateways such as Stripe or PayPal.
- Automated payment processing systems utilizing standardized API protocols, reducing errors and enhancing transaction tracking.
- Compliance automation tools seamlessly handling regulatory requirements like PSD2 and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) checks.
These features enable digital banks to benefit from secure, scalable, and robust API integrations, ensuring reliable payment processing across diverse platforms and regions.
Financial Integrations
Digital banking platforms excel at connecting with essential business software:
- Direct integrations with accounting tools such as QuickBooks, Xero, or Sage.
- Payroll system integrations like Gusto or ADP.
- Connectivity with invoicing platforms such as FreshBooks or Zoho Invoice.
- Integration with expense management software like Expensify or Concur.
- API-based integrations with platforms like Plaid for secure financial application connectivity.
- DocuSign integration for streamlined digital document management.
It allows businesses to benefit by automating financial workflows, eliminating manual data entry, and simplifying reconciliation.
Robust Security and Fraud Protection
Security is a top priority for digital banks:
- Advanced data encryption protocols such as AES-256 and TLS protecting transactions and stored data.
- Real-time AI-driven fraud detection systems like Feedzai or Featurespace that identify and mitigate suspicious activities instantly.
- Automated compliance processes meeting regulatory standards such as KYC, GDPR, and AML regulations.
- Adaptive authentication solutions provided by identity management platforms like ForgeRock, supporting secure user access management through standards such as OAuth2.0 and OpenID Connect.
These robust security features ensure businesses are protected against financial loss and regulatory risks, while developers value the integration of advanced and compliant security protocols.
Inside the “Cabin”: Digital Banking, User’s View
Digital banks deliver exceptional user experiences through intuitive technology designed to simplify business finance management:
- Intuitive Mobile Apps and Web Portals: Apps like those from Revolut Business and Starling Bank offer sleek, user-centric designs enabling smooth navigation and quick access to essential financial tasks.
- 24/7 Availability: Businesses enjoy uninterrupted access to their accounts anytime and anywhere, significantly enhancing operational flexibility.
- Clear Financial Dashboards: Real-time reporting and budgeting tools, supported by API integrations (Plaid), give businesses clear visibility into their financial health.
- Proactive Notifications: Platforms frequently leverage real-time notifications, alerting users immediately about important account activities or upcoming financial obligations.
In many cases, to create user-friendly interfaces, Itexus utilizes frameworks like React Native for mobile apps, Angular for web portals, and scalable cloud infrastructure (AWS, Azure), ensuring businesses receive responsive, reliable, and engaging financial platforms.
Cost of Developing Digital Banking Applications
Understanding the development costs of digital banking applications helps businesses plan effectively. Here’s a concise breakdown of what typically influences these costs:
Application Complexity:
- Basic functionalities (account management, payments): $50,000–$100,000.
- Advanced features (AI analytics, personalized dashboards): $150,000–$300,000+.
Technology Choices:
- Frameworks like React Native (mobile) or Angular/React (web): $30,000–$70,000.
- Cloud infrastructure (AWS, Azure): setup and management $20,000–$50,000.
Security Requirements:
- Implementation of robust platforms such as ForgeRock or Okta: $20,000–$50,000.
- Compliance with regulations (GDPR, KYC, AML): $15,000–$30,000.
Integrations:
- Third-party APIs (Plaid, DocuSign, Stripe): $10,000–$30,000.
Typical Cost Breakdown:
- UI/UX Design: $15,000–$40,000.
- Backend & Infrastructure: $50,000–$100,000.
- API Integration: $15,000–$35,000.
- Security Features: $20,000–$50,000.
- Testing & QA: $10,000–$20,000.
- Annual Maintenance & Support: approximately 20%–30% of initial costs.
Cost Optimization Tips:
At Itexus, we strive to reduce costs by offering workable solutions, including:
- Developing a Minimum Viable Product (MVP)—a simplified initial version of the product designed to validate core functionalities and gather user feedback before investing in additional features.
- Leveraging modular architectures and existing fintech solutions.
- Using cloud-based services strategically for scalability and cost efficiency.
By balancing cost-efficiency, security, and usability, businesses can achieve optimal results. Experienced fintech developers like Itexus can help you navigate these trade-offs and implement secure, efficient, and user-friendly technology solutions that drive superior customer experiences.
Recommendations by Itexus as a conclusion
To effectively balance innovation with security, we recommend an incremental approach, starting with customer-facing processes and integrating core systems through APIs and cloud solutions, ensuring a secure and compliant digital banking experience. This approach yields significant benefits, as evidenced by our successful transformations at Itexus, where we’ve modernized legacy systems and automated workflows using robust technologies, resulting in streamlined processes and improved customer engagement, ultimately driving business growth and efficiency in the digital banking sector.
Q: How long does it typically take to develop a custom digital banking application, and what are the key factors that influence the development timeline?
A: The development timeline for a custom digital banking application can vary depending on the complexity of the project, the technology stack, and the resources allocated. However, on average, it can take anywhere from 6 to 18 months to develop a fully functional digital banking application. Key factors that influence the development timeline include the number of features, the level of customization, and the integration requirements with third-party services.
Q: What are the benefits of using a hybrid digital banking model, and how do they differ from fully digital banks?
A: Hybrid digital banking models offer the benefits of both digital and traditional banking, providing businesses with the flexibility to manage their finances online while still having access to physical branches and in-person support when needed. Compared to fully digital banks, hybrid models are often more suitable for businesses that require occasional cash handling, have complex financial needs, or prefer to have a personal relationship with their bank. However, fully digital banks may offer lower fees, more innovative services, and greater convenience for businesses that are primarily digital.
Q: How do digital banks ensure the security and integrity of customer data, and what measures are in place to prevent cyber attacks and data breaches?
A: Digital banks take data security very seriously and implement robust measures to protect customer data, including advanced encryption protocols, real-time AI-driven fraud detection systems, and adaptive authentication solutions. They also comply with industry standards and regulations, such as GDPR and KYC, to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of customer data. Additionally, digital banks often conduct regular security audits, penetration testing, and employee training to prevent cyber attacks and data breaches, and have incident response plans in place to respond quickly and effectively in the event of a security incident.
